Li ion Battery Charging (CC-CV)
CC-CV Charging of Li-ion Batteries: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
- Constant Current-Constant Voltage (CC-CV) charging is the standard charging protocol for lithium-ion batteries.
- This method ensures safe, efficient, and complete charging while maximizing battery life and performance.
- Understanding this charging algorithm is crucial for battery management system design and optimal battery utilization.
The Water Glass Analogy
To understand CC-CV charging, imagine pouring water into a glass:
Initial Pour (CC Phase):
- When you first start pouring water into an empty glass, you can pour at a steady, high rate.
- The glass accepts water readily, and you maintain a constant flow rate.
- Similarly, when a Li-ion battery is nearly empty, it can accept charge at a constant, high current rate without the voltage rising too quickly.
Approaching Full (CV Phase):
- As the glass nears capacity, you must slow down your pouring rate to avoid overflow.
- You maintain the water level right at the rim (constant level) while gradually reducing the flow rate.
- Similarly, when the battery approaches full charge, the charger maintains a constant voltage while the current naturally decreases as the battery's ability to accept charge diminishes.
Full State:
- Eventually, the water flow stops completely when the glass is full.
- Likewise, the charging current drops to near zero when the battery is fully charged.
CC-CV Charging Process
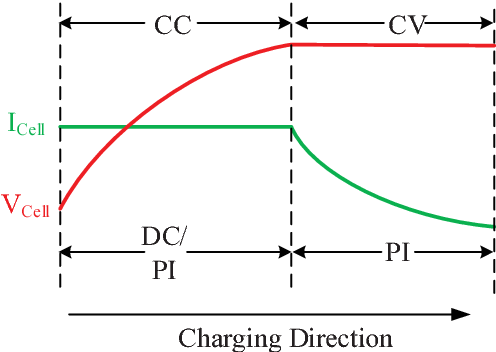
Phase 1: Constant Current (CC)
- Voltage Range: Typically from 2.5-3.0V to 4.2V per cell (these values are for an NMC chemistry cell, values might change for different chemistries)
- Current: Fixed at the specified charging current (e.g., 0.5C, 1C)
- Characteristics:
- Voltage rises linearly with time
- Current remains constant
- Fastest charging phase
- Typically charges battery to 70-80% capacity
Phase 2: Constant Voltage (CV)
- Voltage: Fixed at maximum cell voltage (typically 4.2V ± 0.05V) (these values are for an NMC chemistry cell, values might change for different chemistries)
- Current: Gradually decreases as battery approaches full charge
- Characteristics:
- Current follows exponential decay
- Voltage remains constant
- Slower charging phase
- Charges remaining 20-30% capacity
Phase 3: Termination
- Trigger: Current drops below termination threshold (typically C/20 to C/10)
- Action: Charger stops or switches to trickle/maintenance mode
- Result: Battery is considered fully charged (100% SOC)
Technical Parameters
Voltage Specifications (for a typical NMC cell)
- Nominal Voltage: 3.6V or 3.7V per cell
- Maximum Charge Voltage: 4.2V ± 0.05V per cell
- Minimum Discharge Voltage: 2.5V to 3.0V per cell
Current Specifications
- Charge Rate: Typically 0.5C to 1C (C = battery capacity in Ah)
- Termination Current: C/20 to C/10
- Maximum Current: Limited by battery specifications and thermal constraints
Safety Considerations
Overcharge Protection
- Precise voltage regulation prevents overcharging
- Temperature monitoring prevents thermal runaway
- Current limiting protects against overcurrent conditions
Thermal Management
- Charging should stop if temperature exceeds safe limits (typically 45°C)
- Adequate cooling may be required for fast charging applications
Advantages of CC-CV Charging
- Safety: Prevents overcharging and thermal runaway
- Efficiency: Maximizes energy transfer while minimizing losses
- Battery Life: Reduces stress on battery chemistry
- Simplicity: Straightforward implementation in charging circuits
- Standardization: Widely accepted industry standard
Implementation in Battery Management Systems
Hardware Requirements
- Precision voltage reference and regulation
- Current sensing and control circuitry
- Temperature monitoring
- Safety shutdown mechanisms
Software Control
- State machine implementation for phase transitions
- Real-time monitoring of voltage, current, and temperature
- Fault detection and protection algorithms
Variations and Advanced Techniques
Multi-Stage Charging
- Pre-charging phase for deeply discharged batteries
- Pulse charging for improved efficiency
- Temperature-compensated charging
Fast Charging Adaptations
- Higher current rates with enhanced cooling
- Dynamic current adjustment based on battery condition
- Advanced algorithms for optimal charge time vs. battery health
Conclusion
CC-CV charging represents the optimal balance between charging speed, safety, and battery longevity for lithium-ion batteries. Like carefully filling a glass with water, this method respects the battery's natural limitations while ensuring complete and safe charging. Understanding this fundamental charging algorithm is essential for anyone working with Li-ion battery systems.